Hunamoid Gym学习
最新更新于: 2025年4月17日下午4点00分
GitHub - humanoid-gym是RobotEra(北京星动纪元)公司开源的一个通用人形机器人训练框架,任务为“根据给出的指令进行走路”,训练的仿真环境为IsaacGym,迁移到Mujoco仿真以及其家的XBot-L机器人上,他们还基于该仓库发了另一片文章Advancing Humanoid Locomotion: Mastering Challenging Terrains with Denoising World Model Learning并获得了RSS 2024的Outstanding Paper Award
类似的虚实迁移样例还有宇树的unitree_rl_gym,该仓库很可能是对其进行的改进版本,宇树在23年10月开源,本仓库在24年3月开源,而他们共同参考的应该是legged_gym于21年10月开源
机器人仿真训练包含非常多参数需要调整,本项目架构清晰,除去pytorch, numpy, isaacgym外没有调用其他库,PPO算法也是从rsl_rl中摘取出的(这比宇树的更简洁),因此可以学习代码架构设计;本项目也可以作为运动控制入门,整理仿真与真机中机器人所需的状态信息有哪些,虚实迁移中存在哪些可能问题
由于乐聚机器人Kuavo42就是基于该框架做的第一版RL训练,可以在其机器人上进行模型的虚实迁移测试
前置知识
机器人仿真控制中存在两个频率设置,一个是仿真频率,在humanoid-gym中存在配置文件的sim.dt中,而RL的控制频率通常是以control.decimation个sim.dt为周期去执行动作,也就是RL频率为1/(sim.dt*control.decimation)(IsaacLab中也是用decimation关键字做控制帧抽取的)
当前主流的RL控制方法是:RL的Actor网络输出每个关节的目标角度 ,假设当前的每个关节角度为 ,关节角速度为 ,则通过PD控制计算出,传给仿真的力矩大小为
由于目标关节角速度 一般为 所以略去,在legged_robot.py的_compute_torques或sim2sim.py的pd_control中可以找到实际运用
代码架构分析
以下代码为humanoid-gym v1.0.0版本,也是当前master版本
.
├── humanoid
│ ├── algo
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── ppo
│ │ │ ├── actor_critic.py
│ │ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ │ ├── on_policy_runner.py
│ │ │ ├── ppo.py
│ │ │ └── rollout_storage.py
│ │ └── vec_env.py # 定义VecEnv抽象类, 用于PPO中类声明
│ ├── envs
│ │ ├── base
│ │ │ ├── base_config.py
│ │ │ ├── base_task.py # 定义BaseTask, 虽然没继承VecEnv类, 但覆盖了VecEnv的属性
│ │ │ ├── legged_robot_config.py
│ │ │ ├── legged_robot.py
│ │ │ └── LICENSE
│ │ ├── custom
│ │ │ ├── humanoid_config.py
│ │ │ └── humanoid_env.py
│ │ └── __init__.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── scripts
│ │ ├── play.py
│ │ ├── sim2sim.py
│ │ └── train.py
│ └── utils
│ ├── calculate_gait.py
│ ├── helpers.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── logger.py
│ ├── math.py
│ ├── task_registry.py
│ └── terrain.py
├── logs # 存储训练保存的权重
│ └── XBot_ppo
│ └── exported
│ └── policies
│ └── policy_example.pt
├── README.md
├── resources # 存储机器人定义(URDF或者MJCF文件, 定义Joint, Link, 碰撞, 惯性矩阵等信息)
│ └── robots
│ └── XBot
│ ├── meshes # Mesh部件(对Link进行渲染, 也可构成碰撞体积)
│ │ ├── base_link.STL
│ │ ├── ...
│ │ └── waist_yaw_link.STL
│ └── mjcf # Mujoco定义文件
│ ├── XBot-L-terrain.xml
│ └── XBot-L.xml
└── setup.py环境类
BaseTask
humanoid/envs/base/base_task.py中BaseTask类,具有algo.VecEnv中的所有属性,完成了如下功能:
初始化函数
- IsaacGym:指定计算、渲染设备,启动仿真,加载机器人模型,指定初始相机的朝向、位置
注意:地形、模型的加载是用
creat_sim函数,而该函数由其子类的子类实现(例如XBotLFreeEnv,感觉这个函数由LeggedRobot实现也可以),模型的加载由子类LeggedRobot实现_create_envs
- 制定环境参数:环境数
num_envs,观测维度num_observations,特权观测维度num_privileged_obs,动作维度num_actions - 分配buffer:
obs_buf, privileged_obs_buf, rew_buf, reset_buf, episode_length_buf, time_out_buf等
基础函数
get_observations, get_privileged_observations:分别返回self.obs_buf, self.privileged_obs_bufreset_idx(env_ids: list)(待实现):重置指定编号的机器人reset:调用reset_idx重置所有机器人,并执行一次全0的动作step(actions)(待实现):执行指定动作actionsrender:渲染IsaacGym可视化窗口(渲染进行需要该函数驱动)
LeggedRobot
humanoid/envs/base/legged_robot.py中LeggedRobot是对BaseTask类的继承,最核心的环境类,完成对MDP过程的全部处理,实际训练或推理中由TaskRegistry.make_env进行实例化:
init
初始化环境,调用父类BaseTask的__init__创建IsaacGym仿真,进而调用create_sim将机器人放入仿真
_parse_cfg
将传入的env_cfg解析出所需的
dt:RL推理的时间间隔(单位:s)obs_scales:obs和reward的缩放系数进行重命名reward_scales, command_ranges:奖励系数和命令的随机范围,从类转为字典max_episode_length:当前RL推理轨迹最大长度(类似gymnasium中的truncated)push_interval:计算随机推力产生的RL间隔步数
_prepare_reward_function
- 将所有的
reward_scales乘上dt,保证累计量统一 - 获取
LeggedRobot子类中的所有_reward_{REWARD_NAME}载入reward_names, reward_functions中 - 创建
episode_sums用于存储episode总奖励
_init_buffers
本体感知
初始化状态信息存储的buffer,这里介绍了所有仿真中可以获取到的状态信息,包括机器人的本体感知:
下文表示弧度,表示牛,角标表示世界坐标系下三个方向的分量,无特殊说明,四元数的默认顺序为
在IsaacGym或IsaacSim中,会把URDF中的Link或MJCF中的Body称为Rigid(刚体),也即Joint连接的两个对象,下文也按刚体来称呼
dof_state关节信息dof_pos关节位置(单位 )dof_vel关节速度(单位 )
root_states机器人基座相对世界坐标系的信息( 维,与下文中的rigid_state状态信息一致)base_quat基座坐标系姿态变换到世界坐标系的四元数(可通过IMU获得)base_euler_xyz(从base_quat转换)基座坐标系姿态变换到世界坐标系的欧拉角(表示 )
base_lin_vel机器人基座相对世界坐标系的线速度(通过root_states和base_quat逆变换得到)base_ang_vel机器人基座相对世界坐标系的角速度(通过root_states和base_quat逆变换得到)gravity_vec沿重力方向的单位向量,在这里是projected_gravity将机器人基座坐标系下的gravity_vec逆变换到世界坐标系下,也就是世界坐标系下机器人的垂直方向
控制相关
torques每个关节执行的力矩(单位 )p_gains, d_gainsPD控制器的比例增益和微分增益系数(单位 ,)actions当前帧预测的动作,例如位控(单位 )last_actions, last_last_actions上帧以及上上帧预测的动作default_dof_pos, default_joint_pd_target初始的关节角度rand_push_force随机推力(root_states线速度加入噪声)rand_push_torque随机力矩(root_states角速度加入噪声)
指令相关
commands目标指令,期望线速度、角速度、偏航角速度、偏航角(),第三个和第四个指令仅选其一,当heading_command=True时使用作为控制指令,否则用commands_scale命令输入到模型时的缩放比例系数(仅对进行缩放)
环境相关
contact_forces机器人刚体与环境的接触力(表示 ),用于判断环境终止、奖励设计rigid_state刚体的完整状态( 维),表示如下:- 位置:单位
- 姿态四元数
- 线速度:单位
- 角速度:单位
feet_air_time每个足部刚体在空中的时间(单位 )last_contacts上帧是否接触地面height_points机器人周围地形采样点的坐标(单位 )p.s.可能是地形高度measured_heights采样点处测量的地形高度(单位 )
配置类
LeggedRobotCfg
命令行参数解析与任务注册表
实例化环境需要进行任务相关参数解析,具体流程如下:
from humanoid.utils import get_args, task_registry
# humanoid/envs/__init__.py 注册环境
task_registry.register("env_name", task_class, env_cfg, train_cfg)
# train.py 或 play.py 使用环境
env_cfg, train_cfg = task_registry.get_cfgs("env_name")
# 这里可以修改一些默认的env_cfg, train_cfg信息...
# 解析命令行信息
args = get_args()
# 实例化环境 (后面两个参数可以为空, 则会默认调用get_args()和默认的env_cfg)
env = task_registry.make_env("env_name", args, env_cfg)
# 实例化训练执行器类
runner, train_cfg = task_registry.make_alg_runner(env, "env_name", args, train_cfg)TaskRegistry
humanoid/utils/task_registry.py中TaskRegistry类用于管理任务,环境配置,训练配置信息,具体函数细节如下:
register
# 例如注册新的任务
task_registry.register("humanoid_ppo", XBotLFreeEnv, XBotLCfg(), XBotCfgPPO())其中:
name:str描述的任务名称task_class:环境类继承于VecEnv,也是继承于LeggedRobot,包含MDP的所有过程env_cfg:环境配置类,继承于LeggedRobotCfgtrain_cfg:训练配置类,继承于LeggedRobotCfgPPO
get_cfgs
根据env_name将默认的env_cfg和train_cfg返回
make_env
- 参数解析:通过
update_cfg_from_args将args中的参数读取到env_cfg中,支持无参数通过name进行初始化(train中启动的方法),通过传入env_cfg进行有参数初始化(play中启动的方法) - 设置随机种子(env_cfg中的随机种子会复制train_cfg的种子,但是
args.seed只会对) - 利用
class_to_dict(env_cfg.sim)和parse_sim_params获得仿真物理引擎的配置类sim_params - 获得实例化对应的环境类,得到
env和配置参数env_cfg
make_alg_runner
- 参数解析:通过
update_cfg_from_args将args中的参数读取到train_cfg中,支持无参数通过name进行初始化(train中启动的方法),通过传入train_cfg进行有参数初始化(play中启动的方法) - 基于
log_root创建训练日志保存路径,默认为:ROOT/logs/<experiment_name>/<datetime>_<run_name> - 通过
eval(train_cfg.runner_class_name)直接获取训练执行器类名称(默认只有algo.ppo.on_policy_runner) - 实例化训练器得到
runner - 通过
train_cfg.runner.resume也是args.resume判断是否加载模型继续训练,加载模型逻辑如下:- 判断checkpoint文件夹是否以
run_name结尾 - 如果
load_run=-1默认对文件按照日期排序,获得最后一次模型对应文件夹,否则加载指定的load_run文件夹 - 如果
checkpoint=-1默认对文件保存节点排序,通过"{0:0>15}".format(m)利用数字0的ASCII码值小于字母和_来补位比较,否则加载指定的checkpoint文件 - 返回最后找到的
*.pt模型文件
- 判断checkpoint文件夹是否以
- 返回最终得到的
runner, train_cfg
RSL_RL训练器
由IsaacGym成员开发,一个用PyTorch在GPU上高效训练PPO的训练器GitHub - rsl_rl,要求仿真环境的状态都是通过torch.tensor在GPU上可直接获取到,是IsaacGym, IsaacSim, Genesis的基准算法,在HumanoidGym中将最早的v1.0.2核心代码抽取出来,加上了wandb日志记录,并优化了部分细节、代码格式
RSL_RL版本的PPO和经典PPO的主要区别在与Critic网络输入可以是特权观测(Privileged Obs)
一个PPO训练器包含四个部分:
runner:训练循环,日志记录,模型保存/读取管理,模型相关代码algorithm:PPO算法执行,动作预测,在线数据收集,Actor/Critic损失计算,模型更新,module:网络结构设计,经典全连接形式的ActorCritic,连续动作的分布采样storage:数据存储,GAE计算,训练batch生成器
上述三个配置分别对应*CfgPPO中的runner, algorithm, policy类
on_policy_runner
在线策略训练器类OnPolicyRunner,可拓展的算法例如PPO, TD3, DDPG等
init
- 初始化参数配置文件
cfg, alg_cfg, policy_cfg,分别对应runner, algorithm, policy的配置文件 - 实例化神经网络类
policy_class_name,例如ActorCritic - 实例化算法类
algorithm_class_name,例如alg_class - 实例化算法的buffer类
- 创建日志相关属性,例如
log_dir, writer, tot_timesteps等,但没有实例化,在执行learn时进行实例化 - 执行一次
env.reset,并舍弃返回值
在执行learn时候进行初始化,好处可以在play时避免创建空的训练日志
learn
- 初始化日志writer,包括wandb,tensorboard
- 传入的
init_at_random_ep_len=True会在最大episode长度内,随机每个环境的第一次的episode长度,这会对phase(如果状态输入有),time_out_buffer,commands.resampling_time产生影响 - 创建
rewbuffer, lenbuffer以及辅助记录的cur_reward_sum, cur_episode_length,这些局部变量都将通过locals()传给log(locals())处理 - 在
OnPolicyRunner中
实际训练环境分析
XBotLFreeEnv
Reward
奖励系数reward.scales参考humanoid/envs/custom/humanoid_config.py,奖励函数位于humanoid/envs/custom/humanoid_env.py和humanoid/envs/base/legged_robot.py,命名格式为_reward_{name},对于误差奖励函数通用格式如下
总计使用22个奖励,具体如下表所示:
| # | 名称 | 系数 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | joint_pos | 1.6 | 当前关节位置与目标关节位置(由 函数给出)误差 |
| 2 | feet_clearance | 1. | 达到目标抬脚高度的滞空奖励(取值) |
| 3 | feet_contact_number | 1.2 | 与地面接触是否和抬脚周期对齐( 对齐,否则 ) |
| gait | |||
| 4 | feet_air_time | 1. | 脚的滞空时长奖励(范围) |
| 5 | foot_slip | -0.05 | 脚接触地面时发生的滑步惩罚(水平面上移动速度范数开根号) |
| 6 | feet_distance | 0.2 | 两脚的间距奖励(范围) |
| 7 | knee_distance | 0.2 | 两膝盖的间距奖励(范围,最大范围减少) |
| contact | |||
| 8 | feet_contact_forces | -0.01 | 脚与地面接触力大小超过最大接触力max_contact_force的惩罚(范围) |
| vel tracking | |||
| 9 | tracking_lin_vel | 1.2 | 基座线速度与目标线速度误差(范围,拉伸系数) |
| 10 | tracking_ang_vel | 1.1 | 基座偏航速度与目标偏航速度误差(范围,拉伸系数) |
| 11 | vel_mismatch_exp | 0.5 | 对无控制命令的向对齐(范围) |
| 12 | low_speed | 0.2 | 对和目标相对大小和正负性进行分类讨论(取值 ) |
| 13 | track_vel_hard | 0.5 | 基座线速度、偏航速度与目标命令的误差(仅有上界,该奖励将tracking_lin/ang_vel包含) |
| base pos | |||
| 14 | default_joint_pos | 0.5 | 关节与初始关节的误差(次要项)与左右大腿翻滚与偏航角的指数误差(主要项)(范围) |
| 15 | orientation | 1. | 机器人的翻滚角和俯仰角的范数,以及重力投影的范数,做经过指数误差函数求和平均(范围 |
| 16 | base_height | 0.2 | 机器人基座到脚底板距离,和目标基座高度误差(范围) |
| 17 | base_acc | 0.2 | 机器人基座加速度的范数做指数误差(范围,此处加速度是真实加速度的倍) |
| energy | |||
| 18 | action_smoothness | -0.002 | 考虑当前帧、上帧和上上帧的动作误差平方以及当前动作的范数 |
| 19 | torques | -1e-5 | 当前全部关节力矩的范数平方 |
| 20 | dof_vel | -5e-4 | 当前全部关节的角速度范数平方 |
| 21 | dof_acc | -1e-7 | 当前全部关节的角加速度范数平方 |
| 22 | collision | -1. | 上身刚体base_link是否产生接触力 |
设
| # | 名称 | 系数 | 对标 | 含义 | 公式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lin. velocity tracking | 1.0 | tracking_lin_vel, vel_mismatch_exp | 线速度误差控制 | |
| 2 | Ang. velocity tracking | 1.0 | tracking_ang_vel, vel_mismatch_exp | 角速度误差控制 | |
| 3 | Orientation tracking | 1.0 | orientation | 翻滚角和俯仰角误差 | |
| 4 | Base height tracking | 0.5 | base_height | base_link的z轴高度误差 |
|
| 5 | Periodic Force | 1.0 | feet_contact_number | 周期脚接触力 | |
| 6 | Periodic Velocity | 1.0 | 周期脚移动速度 | ||
| 7 | Foot height tracking | 1.0 | feet_clearance | 抬脚到指定高度 | |
| 8 | Foot vel tracking | 0.5 | 抬脚到指定速度 | ||
| 9 | Default Joint | 0.2 | default_joint_pos | 与初始状态误差 | |
| 10 | Energy Cost | -1e-4 | torques,dof_vel | 全部关节力矩与角速度范数乘积 | |
| 11 | Action Smoothness | -1e-2 | action_smoothness | 当前帧、上帧、上上帧动作误差 | |
| 12 | Feet movements | -1e-2 | foot_slip | 脚在z轴方向上线速度和加速度 | |
| 13 | Large contact | -1e-2 | feet_contact_forces | 两腿与地面最大接触力大小 |
其中
joint_pos
奖励系数 ,设 为当前关节位置dof_pos与目标关节位置ref_dof_pos的误差,奖励为
def _reward_joint_pos(self):
"""
Calculates the reward based on the difference between the current joint positions and the target joint positions.
"""
joint_pos = self.dof_pos.clone() # shape=(N, 12)
pos_target = self.ref_dof_pos.clone()
diff = joint_pos - pos_target
r = torch.exp(-2 * torch.norm(diff, dim=1)) - 0.2 * torch.norm(diff, dim=1).clamp(0, 0.5)
return r
# 其中ref_dof_pos计算方式如下
def compute_ref_state(self):
phase = self._get_phase()
sin_pos = torch.sin(2 * torch.pi * phase)
sin_pos_l = sin_pos.clone()
sin_pos_r = sin_pos.clone()
self.ref_dof_pos = torch.zeros_like(self.dof_pos)
scale_1 = self.cfg.rewards.target_joint_pos_scale
scale_2 = 2 * scale_1
# left foot stance phase set to default joint pos
sin_pos_l[sin_pos_l > 0] = 0 # 左脚都是负的(向前抬是向负变换)
# 以下均为俯仰关节(绕y旋转)
self.ref_dof_pos[:, 2] = sin_pos_l * scale_1 # 大腿
self.ref_dof_pos[:, 3] = sin_pos_l * scale_2 # 膝盖
self.ref_dof_pos[:, 4] = sin_pos_l * scale_1 # 踝
# right foot stance phase set to default joint pos
sin_pos_r[sin_pos_r < 0] = 0 # 右脚的都是正的(向前抬是向正变换)
self.ref_dof_pos[:, 8] = sin_pos_r * scale_1
self.ref_dof_pos[:, 9] = sin_pos_r * scale_2
self.ref_dof_pos[:, 10] = sin_pos_r * scale_1
# Double support phase
self.ref_dof_pos[torch.abs(sin_pos) < 0.1] = 0
# 在env配置中存在参数use_ref_actions, 在actions基础上加上这个ref_action, 没有启用
self.ref_action = 2 * self.ref_dof_pos
# phase计算方法如下
def _get_phase(self):
cycle_time = self.cfg.rewards.cycle_time # cycle_time=0.64即一个抬起左右脚的周期(先右脚后左脚)
phase = self.episode_length_buf * self.dt / cycle_time
return phase # 返回周期数feet_clearance
奖励系数 ,feet_indices分别为左和右脚踝翻滚(x轴旋转)关节,设 为当前抬脚高度与目标抬脚高度误差target_feet_height,奖励为
def _reward_feet_clearance(self):
"""
Calculates reward based on the clearance of the swing leg from the ground during movement.
Encourages appropriate lift of the feet during the swing phase of the gait.
"""
# Compute feet contact mask
contact = self.contact_forces[:, self.feet_indices, 2] > 5.
# Get the z-position of the feet and compute the change in z-position
feet_z = self.rigid_state[:, self.feet_indices, 2] - 0.05
delta_z = feet_z - self.last_feet_z
self.feet_height += delta_z # 通过累计量计算脚高度z
self.last_feet_z = feet_z
# Compute swing mask
swing_mask = 1 - self._get_gait_phase()
# feet height should be closed to target feet height at the peak
rew_pos = torch.abs(self.feet_height - self.cfg.rewards.target_feet_height) < 0.01
rew_pos = torch.sum(rew_pos * swing_mask, dim=1)
self.feet_height *= ~contact # 重置接触地面脚的高度
return rew_pos
# 对腿部是否不抬起的mask, 不抬起为1, 抬起为0, 第一维为左腿, 第二维为右腿
def _get_gait_phase(self):
# return float mask 1 is stance, 0 is swing
phase = self._get_phase()
sin_pos = torch.sin(2 * torch.pi * phase)
# Add double support phase
stance_mask = torch.zeros((self.num_envs, 2), device=self.device)
# left foot stance
stance_mask[:, 0] = sin_pos >= 0
# right foot stance
stance_mask[:, 1] = sin_pos < 0
# Double support phase
stance_mask[torch.abs(sin_pos) < 0.1] = 1
return stance_mask # shape=(N, 2)feet_contact_number
奖励系数 ,脚接触奖励,设 为是否接触,,则奖励为
def _reward_feet_contact_number(self):
"""
Calculates a reward based on the number of feet contacts aligning with the gait phase.
Rewards or penalizes depending on whether the foot contact matches the expected gait phase.
"""
contact = self.contact_forces[:, self.feet_indices, 2] > 5.
stance_mask = self._get_gait_phase()
reward = torch.where(contact == stance_mask, 1.0, -0.3)
return torch.mean(reward, dim=1)feet_air_time
奖励系数 ,设一只脚的滞空时间为 ,则奖励为
def _reward_feet_air_time(self):
"""
Calculates the reward for feet air time, promoting longer steps. This is achieved by
checking the first contact with the ground after being in the air. The air time is
limited to a maximum value for reward calculation.
"""
contact = self.contact_forces[:, self.feet_indices, 2] > 5.
stance_mask = self._get_gait_phase()
# 对触地的mask, 包含当前contact, 上帧contact, 目标stand mask, 三者的异或
self.contact_filt = torch.logical_or(torch.logical_or(contact, stance_mask), self.last_contacts)
self.last_contacts = contact
first_contact = (self.feet_air_time > 0.) * self.contact_filt
self.feet_air_time += self.dt
air_time = self.feet_air_time.clamp(0, 0.5) * first_contact
self.feet_air_time *= ~self.contact_filt
return air_time.sum(dim=1)foot_slip
惩罚系数 ,设脚接触地面时的x,y方向上的移动速度为 ,则奖励为
def _reward_foot_slip(self):
"""
Calculates the reward for minimizing foot slip. The reward is based on the contact forces
and the speed of the feet. A contact threshold is used to determine if the foot is in contact
with the ground. The speed of the foot is calculated and scaled by the contact condition.
"""
contact = self.contact_forces[:, self.feet_indices, 2] > 5.
foot_speed_norm = torch.norm(self.rigid_state[:, self.feet_indices, 7:9], dim=2)
rew = torch.sqrt(foot_speed_norm)
rew *= contact
return torch.sum(rew, dim=1)feet_distance
奖励系数 ,设
当前左右脚的水平距离为,则奖励为
其中
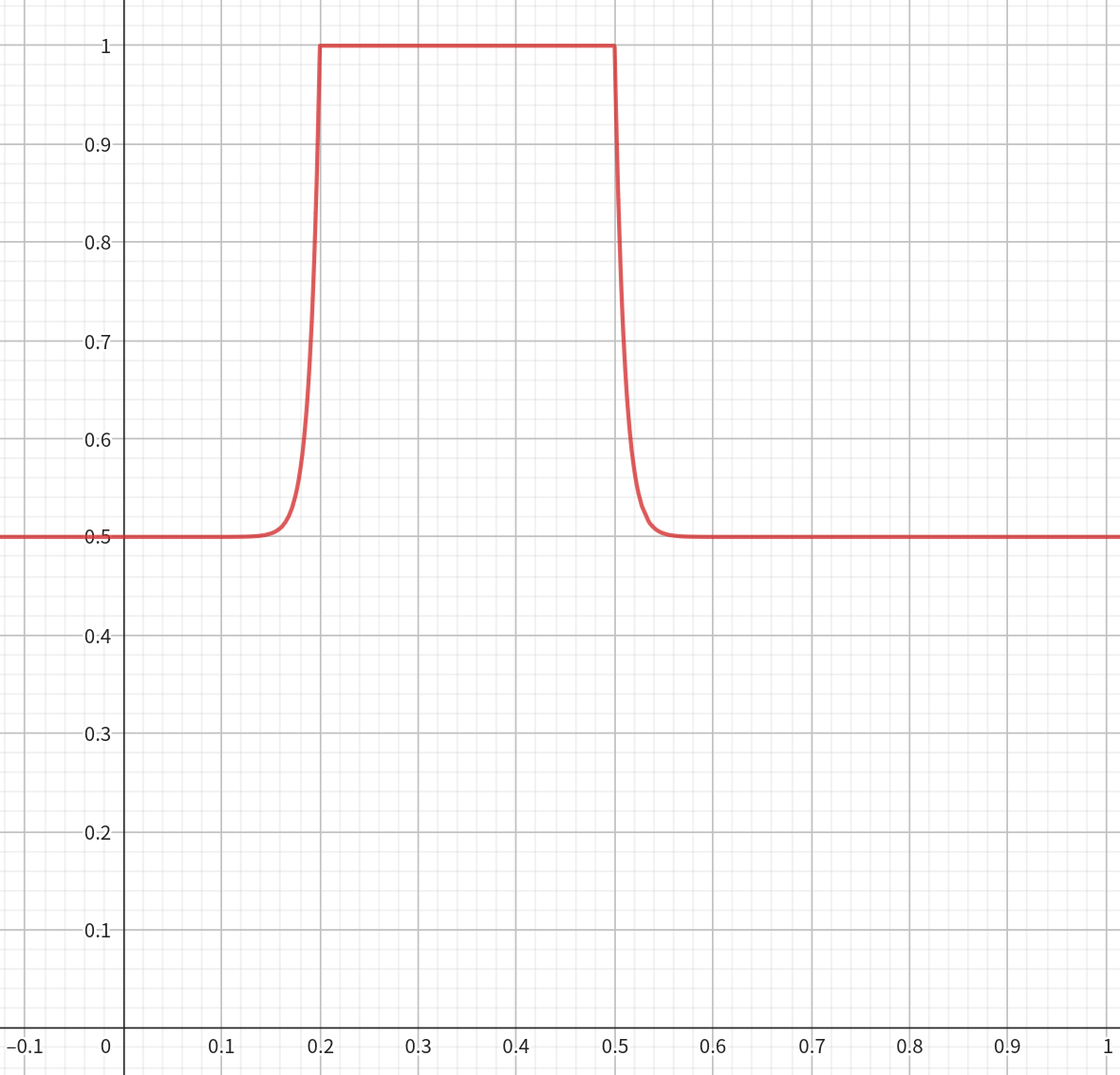
def _reward_feet_distance(self):
"""
Calculates the reward based on the distance between the feet. Penalize feet get close to each other or too far away.
"""
foot_pos = self.rigid_state[:, self.feet_indices, :2]
foot_dist = torch.norm(foot_pos[:, 0, :] - foot_pos[:, 1, :], dim=1)
fd = self.cfg.rewards.min_dist # 0.2
max_df = self.cfg.rewards.max_dist # 0.5
d_min = torch.clamp(foot_dist - fd, -0.5, 0.)
d_max = torch.clamp(foot_dist - max_df, 0, 0.5)
return (torch.exp(-torch.abs(d_min) * 100) + torch.exp(-torch.abs(d_max) * 100)) / 2knee_distance
膝盖间距奖励,和feet_distance唯一区别就是减少了,再更小范围内给予高奖励
def _reward_knee_distance(self):
"""
Calculates the reward based on the distance between the knee of the humanoid.
"""
foot_pos = self.rigid_state[:, self.knee_indices, :2]
foot_dist = torch.norm(foot_pos[:, 0, :] - foot_pos[:, 1, :], dim=1)
fd = self.cfg.rewards.min_dist
max_df = self.cfg.rewards.max_dist / 2 # 和feet_distance的唯一区别
d_min = torch.clamp(foot_dist - fd, -0.5, 0.)
d_max = torch.clamp(foot_dist - max_df, 0, 0.5)
return (torch.exp(-torch.abs(d_min) * 100) + torch.exp(-torch.abs(d_max) * 100)) / 2feet_contact_forces
惩罚系数 ,设当前脚与地面的接触力为 (考虑三维空间),则奖励为
其中
def _reward_feet_contact_forces(self):
"""
Calculates the reward for keeping contact forces within a specified range. Penalizes
high contact forces on the feet.
"""
return torch.sum((torch.norm(self.contact_forces[:, self.feet_indices, :], dim=-1) - self.cfg.rewards.max_contact_force).clip(0, 400), dim=1)tracking_lin_vel
奖励系数 ,设水平方向上目标速度为 ,机器人基座相对世界坐标系的水平方向上线速度为 ,则奖励为
其中 为tracking_sigma=0.25
def _reward_tracking_lin_vel(self):
"""
Tracks linear velocity commands along the xy axes.
Calculates a reward based on how closely the robot's linear velocity matches the commanded values.
"""
lin_vel_error = torch.sum(torch.square(
self.commands[:, :2] - self.base_lin_vel[:, :2]), dim=1)
return torch.exp(-lin_vel_error * self.cfg.rewards.tracking_sigma)tracking_ang_vel
奖励系数 ,设目标偏航速度为 ,机器人基座相对世界坐标的偏航速度为 ,则奖励为
def _reward_tracking_ang_vel(self):
"""
Tracks angular velocity commands for yaw rotation.
Computes a reward based on how closely the robot's angular velocity matches the commanded yaw values.
"""
ang_vel_error = torch.square(
self.commands[:, 2] - self.base_ang_vel[:, 2])
return torch.exp(-ang_vel_error * self.cfg.rewards.tracking_sigma)vel_mismatch_exp
奖励系数 ,对无控制指令的z轴线速度 、翻滚角速度 、俯仰角速度 向 对齐,则奖励为
def _reward_vel_mismatch_exp(self):
"""
Computes a reward based on the mismatch in the robot's linear and angular velocities.
Encourages the robot to maintain a stable velocity by penalizing large deviations.
"""
lin_mismatch = torch.exp(-torch.square(self.base_lin_vel[:, 2]) * 10)
ang_mismatch = torch.exp(-torch.norm(self.base_ang_vel[:, :2], dim=1) * 5.)
c_update = (lin_mismatch + ang_mismatch) / 2.
return c_updatelow_speed
奖励系数 ,设在机器人坐标系下方向目标线速度为,基座线速度为,则奖励为
def _reward_low_speed(self):
"""
Rewards or penalizes the robot based on its speed relative to the commanded speed.
This function checks if the robot is moving too slow, too fast, or at the desired speed,
and if the movement direction matches the command.
"""
# Calculate the absolute value of speed and command for comparison
absolute_speed = torch.abs(self.base_lin_vel[:, 0])
absolute_command = torch.abs(self.commands[:, 0])
# Define speed criteria for desired range
speed_too_low = absolute_speed < 0.5 * absolute_command
speed_too_high = absolute_speed > 1.2 * absolute_command
speed_desired = ~(speed_too_low | speed_too_high)
# Check if the speed and command directions are mismatched
sign_mismatch = torch.sign(
self.base_lin_vel[:, 0]) != torch.sign(self.commands[:, 0])
# Initialize reward tensor
reward = torch.zeros_like(self.base_lin_vel[:, 0])
# Assign rewards based on conditions
# Speed too low
reward[speed_too_low] = -1.0
# Speed too high
reward[speed_too_high] = 0.
# Speed within desired range
reward[speed_desired] = 1.2
# Sign mismatch has the highest priority
reward[sign_mismatch] = -2.0
return reward * (self.commands[:, 0].abs() > 0.1)track_vel_hard
奖励系数 ,设线速度误差为,偏航角速度误差为 ,指数误差函数为 ,则奖励为
不理解这个奖励为什么就是
tracking_lin_vel,tracking_ang_vel合并,加上一个线性误差项
def _reward_track_vel_hard(self):
"""
Calculates a reward for accurately tracking both linear and angular velocity commands.
Penalizes deviations from specified linear and angular velocity targets.
"""
# Tracking of linear velocity commands (xy axes)
lin_vel_error = torch.norm(
self.commands[:, :2] - self.base_lin_vel[:, :2], dim=1)
lin_vel_error_exp = torch.exp(-lin_vel_error * 10)
# Tracking of angular velocity commands (yaw)
ang_vel_error = torch.abs(
self.commands[:, 2] - self.base_ang_vel[:, 2])
ang_vel_error_exp = torch.exp(-ang_vel_error * 10)
linear_error = 0.2 * (lin_vel_error + ang_vel_error)
return (lin_vel_error_exp + ang_vel_error_exp) / 2. - linear_errordefault_joint_pos
奖励系数 ,设全部关节与默认位置误差为 ,左右大腿翻滚和偏航与默认位置的误差分别为 ,则奖励为
此处指数误差中的
-100系数就是期望
def _reward_default_joint_pos(self):
"""
Calculates the reward for keeping joint positions close to default positions, with a focus
on penalizing deviation in yaw and roll directions. Excludes yaw and roll from the main penalty.
"""
joint_diff = self.dof_pos - self.default_joint_pd_target # default_joint_pd_target就是default_joint_angles
left_yaw_roll = joint_diff[:, :2] # 左大腿关节的翻滚和偏航
right_yaw_roll = joint_diff[:, 6: 8] # 右大腿关节的翻滚和偏航
yaw_roll = torch.norm(left_yaw_roll, dim=1) + torch.norm(right_yaw_roll, dim=1)
yaw_roll = torch.clamp(yaw_roll - 0.1, 0, 50)
return torch.exp(-yaw_roll * 100) - 0.01 * torch.norm(joint_diff, dim=1)orientation
奖励系数 ,设当前基座相对于世界坐标系的翻滚、俯仰角为 ,机器人坐标系下的重力(沿z轴的单位向量)在世界坐标系下的投影为 ,则奖励为
def _reward_orientation(self):
"""
Calculates the reward for maintaining a flat base orientation. It penalizes deviation
from the desired base orientation using the base euler angles and the projected gravity vector.
"""
quat_mismatch = torch.exp(-torch.sum(torch.abs(self.base_euler_xyz[:, :2]), dim=1) * 10)
orientation = torch.exp(-torch.norm(self.projected_gravity[:, :2], dim=1) * 20)
return (quat_mismatch + orientation) / 2.base_height
奖励系数 ,设当前应该在地面上的脚的平均z轴高度为 ,则基座当前z轴高度为 ,可得当前脚部到基座高度为 ,则奖励为
其中
此处
0.05可能是脚踝翻滚关节与脚底板之间距离
def _reward_base_height(self):
"""
Calculates the reward based on the robot's base height. Penalizes deviation from a target base height.
The reward is computed based on the height difference between the robot's base and the average height
of its feet when they are in contact with the ground.
"""
stance_mask = self._get_gait_phase()
measured_heights = torch.sum(
self.rigid_state[:, self.feet_indices, 2] * stance_mask, dim=1) / torch.sum(stance_mask, dim=1)
base_height = self.root_states[:, 2] - (measured_heights - 0.05)
return torch.exp(-torch.abs(base_height - self.cfg.rewards.base_height_target) * 100)base_acc
奖励系数 ,设当前基座相对世界坐标系的速度为 ,上一时刻的相对速度为 ,则奖励为
这里不清楚为什么不是 计算当前加速度,是将 看作常数项了?
def _reward_base_acc(self):
"""
Computes the reward based on the base's acceleration. Penalizes high accelerations of the robot's base,
encouraging smoother motion.
"""
root_acc = self.last_root_vel - self.root_states[:, 7:13]
rew = torch.exp(-torch.norm(root_acc, dim=1) * 3)
return rewaction_smoothness
惩罚系数 ,假设当前帧、上帧、上上帧的动作分别为 ,则奖励为
def _reward_action_smoothness(self):
"""
Encourages smoothness in the robot's actions by penalizing large differences between consecutive actions.
This is important for achieving fluid motion and reducing mechanical stress.
"""
term_1 = torch.sum(torch.square(
self.last_actions - self.actions), dim=1)
term_2 = torch.sum(torch.square(
self.actions + self.last_last_actions - 2 * self.last_actions), dim=1)
term_3 = 0.05 * torch.sum(torch.abs(self.actions), dim=1)
return term_1 + term_2 + term_3torques
惩罚系数 ,设每个关节的力矩为 ,则奖励为
def _reward_torques(self):
"""
Penalizes the use of high torques in the robot's joints. Encourages efficient movement by minimizing
the necessary force exerted by the motors.
"""
return torch.sum(torch.square(self.torques), dim=1)dof_vel
惩罚系数 ,设每个关节的角速度为 ,则奖励为
def _reward_dof_vel(self):
"""
Penalizes high velocities at the degrees of freedom (DOF) of the robot. This encourages smoother and
more controlled movements.
"""
return torch.sum(torch.square(self.dof_vel), dim=1)dof_acc
惩罚系数 ,设每个关节的当前角速度和上一时刻的角速度为 ,则奖励为
def _reward_dof_acc(self):
"""
Penalizes high accelerations at the robot's degrees of freedom (DOF). This is important for ensuring
smooth and stable motion, reducing wear on the robot's mechanical parts.
"""
return torch.sum(torch.square((self.last_dof_vel - self.dof_vel) / self.dt), dim=1)collision
惩罚系数 ,设上身对应刚体base_link的接触力为,则奖励为
def _reward_collision(self):
"""
Penalizes collisions of the robot with the environment, specifically focusing on selected body parts.
This encourages the robot to avoid undesired contact with objects or surfaces.
"""
return torch.sum(1.*(torch.norm(self.contact_forces[:, self.penalised_contact_indices, :], dim=-1) > 0.1), dim=1)